In the modern world of engineering and automation, temperature control is a critical aspect of many systems, from heating and cooling to industrial processes and even everyday appliances. Among the various components that enable precise temperature regulation, thermostatic valves stand out as essential devices. In this blog post, we will explore what thermostatic valves are, how they work, their advantages, and their applications.
What is a Thermostatic Valve?
A thermostatic valve, also known as a temperature control valve, is a device designed to regulate the flow of a fluid (such as water or steam) based on temperature changes. It combines a temperature sensor with a control mechanism to maintain a desired temperature within a system. Unlike manual valves, thermostatic valves operate automatically, making them ideal for systems that require consistent temperature management.
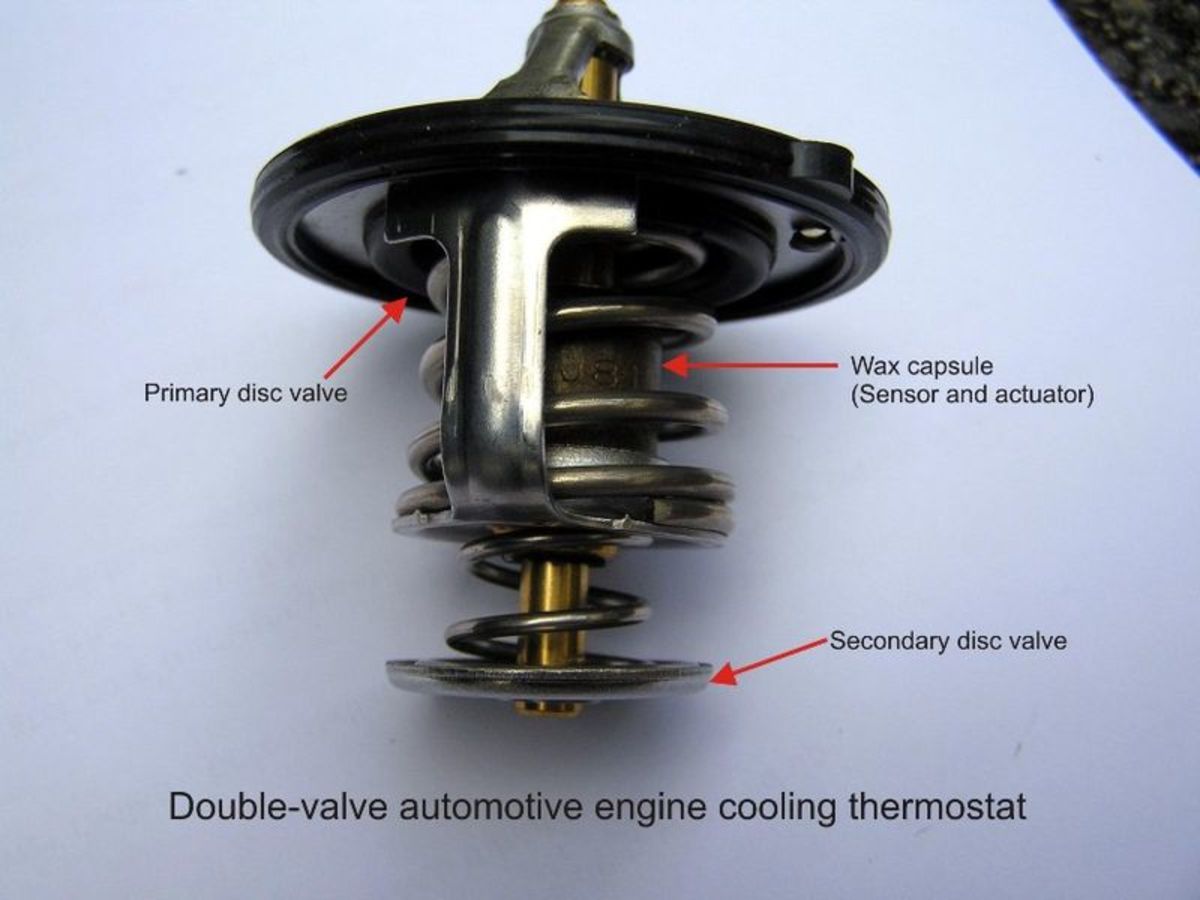
How Does a Thermostatic Valve Work?
The operation of a thermostatic valve relies on a temperature-sensitive element, such as a wax-filled actuator or a bi-metallic strip. When the temperature of the fluid passing through the valve changes, this element expands or contracts, triggering the valve to open or close. This adjustment controls the flow of the fluid, ensuring that the temperature remains within a specified range.For example, in a heating system, if the temperature drops below a set threshold, the thermostatic valve opens to allow more hot water or steam to flow, increasing the heat output. Conversely, if the temperature rises above the desired level, the valve closes to reduce the flow and prevent overheating.
Advantages of Thermostatic Valves
1.Precision Temperature Control
Thermostatic valves provide highly accurate temperature regulation, minimizing fluctuations and ensuring consistent performance in critical applications.
2.Energy Efficiency
By automatically adjusting the flow of heated or cooled fluids, these valves help optimize energy usage, reducing waste and lowering operational costs.
3.Reliability and Longevity
Thermostatic valves are designed to withstand harsh conditions and deliver long-term performance with minimal maintenance.
4.Automation
They eliminate the need for manual intervention, making systems more efficient and easier to manage.
5.Versatility
Thermostatic valves can be adapted to a wide range of applications, from residential heating systems to large-scale industrial processes.

Types of Thermostatic Valves
There are several types of thermostatic valves, each suited for specific applications:
1.Mechanical Thermostatic Valves
These valves use a bi-metallic strip or a wax actuator to mechanically control the flow. They are simple, reliable, and commonly used in residential and commercial systems.
2.Electronic Thermostatic Valves
Equipped with electronic sensors and control systems, these valves offer precise temperature regulation and can be integrated into advanced automation networks.
3.Hydraulic Thermostatic Valves
These valves use hydraulic pressure to control the flow, making them suitable for high-pressure industrial applications.
4.Two-Way and Three-Way Valves
Two-way valves control the flow in a single direction, while three-way valves can divert fluid between two different paths, depending on temperature requirements.
Applications of Thermostatic Valves
Thermostatic valves are widely used across various industries:
1.Heating and Cooling Systems
In residential and commercial buildings, thermostatic valves regulate the flow of hot water or steam in radiators and underfloor heating systems.
2.Industrial Processes
They are crucial in maintaining precise temperatures in manufacturing processes, chemical plants, and power generation systems.
3.Automotive Industry
Thermostatic valves are used in car cooling systems to regulate the flow of coolant, ensuring the engine operates within a safe temperature range.
4.Water Heating Systems
These valves help control the temperature of hot water in boilers and water heaters, preventing overheating and ensuring safety.
5.Solar Energy Systems
Thermostatic valves play a key role in solar thermal systems, managing the flow of heat transfer fluids to optimize energy storage and distribution.

Market Trends and Innovations
The demand for thermostatic valves is growing rapidly, driven by the increasing need for energy efficiency and automation in industries. Recent advancements include:
1.Smart Thermostatic Valves
With the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and remote monitoring capabilities, these valves can be controlled and optimized from a central system or even a smartphone.
2.Improved Materials
The use of high-performance materials, such as stainless steel and corrosion-resistant alloys, enhances durability and extends the lifespan of thermostatic valves.
3.Environmental Regulations
As industries focus on reducing emissions and improving sustainability, thermostatic valves are becoming more popular for their ability to optimize energy consumption.
4.Customization
Manufacturers now offer tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of different industries, ensuring better performance and compatibility.
Conclusion
Thermostatic valves are indispensable in maintaining precise temperature control in a wide range of applications. Their ability to operate automatically, coupled with advancements in technology, makes them a vital component in modern engineering systems. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the role of thermostatic valves will only become more significant.


